It took a while to get back , But I hope I make it worthwhile for the wait 🙂
This week we will read about how to secure resource during runtime and obtain Security Assurance in our environment.
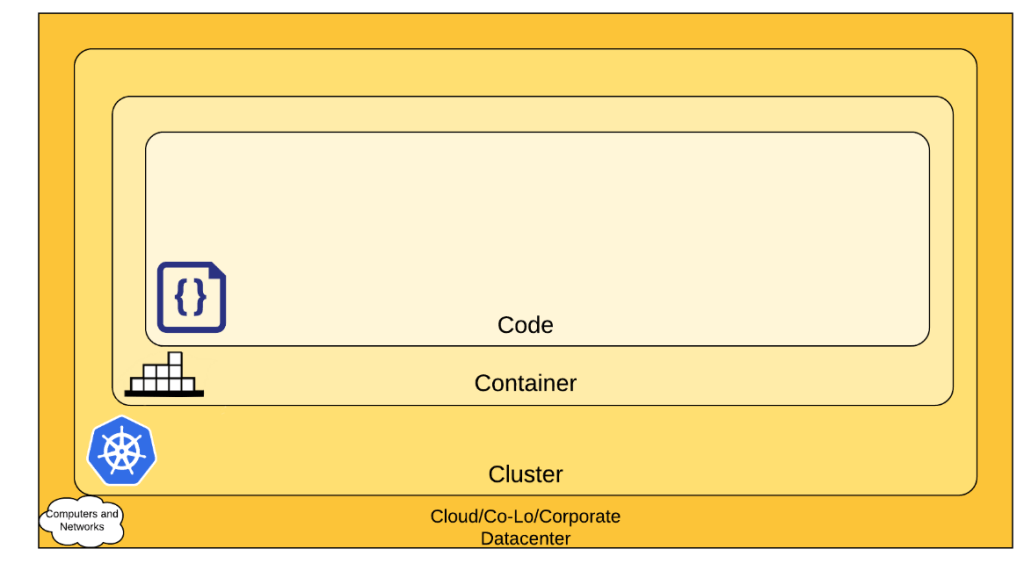
Runtime
Just like previous phases, Develop, Distribute and Deploy. It is crucial to secure resources during the runtime phase. If you interested in securing resources in 3 D’s, I recommend reading it here.

Runtime involves security in three critical areas, compute, access and storage. Compute security should cover from physical to serverless resources. you can use below best practice to implement security across compute resources.
- Compute
- Container
- Read-only OS with services disabled
- Run data with different sensitivity to run in different kernel
- Use Trusted Platform Module (TPM) virtual machine.
- Use Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) (Security Enclaves).
- It protects Data in use, as data is decrypted on the fly within the CPU.
- Secure Orchestration
- Why? It has various attack surface areas Example, access to API, unauthorized access, and access to key-value datastore.
- How? Using security policies, Like
- Resource Request and Limits
- Audit Log analysis
- The Control plane needs to communicate via a periodically rotated certificate.
- Encrypt the secrets
- It is crucial to monitor/secure the Filesystem, Process, and Network.
- Eliminate implicit trust and introduce zero trust (Example via Network policy)
- Use trusted images and encrypt containers.
- Use service mesh for its capability for traffic control, service discovery, load balancing, resilience, 24 observability, and security.
- Detection during runtime (Use tools like Prisma Cloud, Microsoft 365 Defender)
- Container
- Access, In a recent article for Unit42 (Palo Alto), we had a staggering number on why IAM is a target and how it can be the first line of defense. It is essential to follow the principle of least privilege when implementing IAM.
- Users and Applications need to be explicitly authorized (Zero Trust)
- Manage credentials (for example, using HSM)
- Data is where the threat actors up to . In CNS, storage are presented across two technologies. Presented storage , For example, volume, block, and file system storage and Accessed storage, For example, object storage. Security in storage can be implemented using below best practices
- Storage interface points/control plane should be protected against the access controls, authentication, authorization, and potentially encryption in transit.
- Storage stack has multiple layers of functionality, Like how data is stored, retrieved, protected and interacts with an application, orchestrator and/or operating system. So, data has to be protected in various layers.
- Orchestration
- Data access path and inter-node communication
- Protect data in the system or in the service (using parity or mirroring).
- Implement integrity (using checksum)
- Protect caching layer
- Protecting Data services (Like snapshot and replication)
- Protect data in Physical or Non-volatile layers
- Use storage encryption
Security Assurance
- Security Assurance can be implemented using risk management process (Identify and address the risk of the system) and by implementing compliance standards.
- Risk management process, can be implemented by following below methodologies
- Threat Modelling, Example, STRIDE or OCTAVE. It has to be involved during SDLC as well. There are quite a few open source tools to help implement, for example, OWASP Threat Dragon and Microsoft threat modelling tool.
- Use Threat Intelligence to identify/protect against threats and threat actors. It is also possible to identify behavioral indicators like threat actor tactics and techniques based on the activity. MITRE ATT&CK framework is a good place to start.
- It is crucial to have an incident response Management process within the organization, and it involves various phases.
- Preparation
- Detection and Analysis
- Containment, Eradication and Recovery
- Documentation
- Post-Incident Retrospective
- Following Security Principles
- Secure by default
- Least Privilege
- Define roles and responsibility
- Securing supply chain
- Ensuring the security of GitOps
- Implement Zero trust architecture.
- Compliance Standards
- Compliance depends on various factors like where the business is, whom the customer is, where the data is created/consumed, and what is the industry compliance requirement.
- Compliance takes some security benchmarks like CIS and NIST into consideration.
- Few examples
- Card Payment industries require PCI-DSS standards.
- Health care industries HIPAA standard
- European industry needs to adhere to the GDPR standard.
- How to Implement? CSPM tools (Example, Defender for cloud, AWS config, Prisma Cloud)




Leave a comment