NIST Framework has been widely used across organization in different sectors. Now they have released NIST 2 Draft , Let’s see what they have
Each organization have unique
- threats
- Vulnerabilities
- Risk Tolerance
which results in different objectives and approach to the framework in managing the risk. This collectively creates the taxonomy and structure to understand, assess, prioritize, and communicate about cybersecurity risks.
- Understand and Assess
- Describe an organization’s current or target cybersecurity posture
- Determine where an organization may have cybersecurity gaps
- Align policy, business, and technological approaches to managing cybersecurity risks
- Prioritize
- Prioritize opportunities to improve cybersecurity risk management.
- Identify, organize, and prioritize actions for reducing cybersecurity risks
- Inform decisions about cybersecurity-related workforce needs and capabilities.
- Communicate
- Provide a common language for communicating with internal and external parties
- Complement an organization’s risk management process by presenting a concise way for executives and others to distill the fundamental concepts of cybersecurity risk
Framework Core
Let’s understand the core framework of NIST2. Outcome is what organization would like to achieve in terms of cybersecurity risk. And these outcomes are categorized as Functions, Categories and Subcategories and outcomes can be achieved using implementational examples and information references
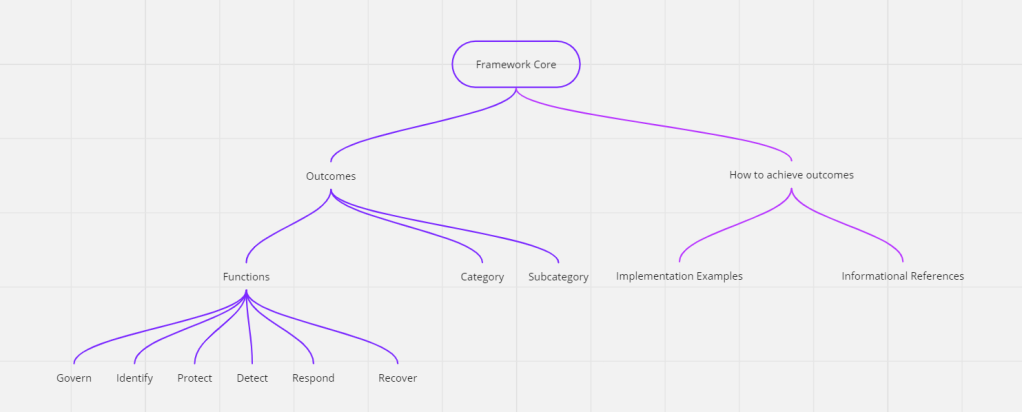

Lets start with understanding Function
Govern
- Establish and monitor the organization’s cybersecurity risk management strategy, expectations, and policy
- The GOVERN Function provides outcomes to inform how an organization will achieve and prioritize the outcomes of the other five Functions in the context of its mission and stakeholder expectations.
- GOVERN directs an understanding of organizational context; the establishment of cybersecurity strategy and cybersecurity supply chain risk management; roles, responsibilities, and authorities; policies, processes, and procedures; and the oversight of cybersecurity strategy.
Identify
- Help determine the current cybersecurity risk to the organization.
- This Function also includes the identification of improvements needed for the organization’s policies, processes, procedures, and practices supporting cybersecurity risk management to inform efforts under all six Functions.
Protect
- Use safeguards to prevent or reduce cybersecurity risk. . Once assets and risks are identified and prioritized, PROTECT supports the ability to secure those assets to prevent or lower the likelihood and impact of adverse cybersecurity events. Outcomes covered by this Function include awareness and training; data security; identity management, authentication, and access control; platform security
Detect
- Find and analyze possible cybersecurity attacks and compromises
- DETECT enables timely discovery and analysis of anomalies, indicators of compromise, and other potentially adverse cybersecurity events that may indicate that cybersecurity attacks and incidents are occurring
Respond
Take action regarding a detected cybersecurity incident.
- RESPOND supports the ability to contain the impact of cybersecurity incidents.
- Outcomes within this Function cover incident management, analysis, mitigation, reporting, and communication
Recover
- Restore assets and operations that were impacted by a cybersecurity incidents.
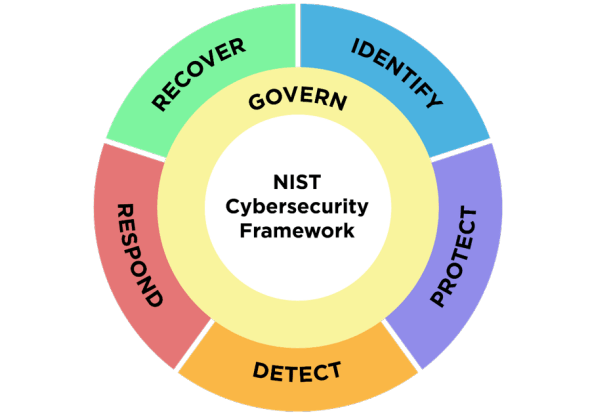
Categories are the subdivisions of a Function into groups of related cybersecurity outcomes.
Subcategories further divide a Category into specific outcomes of technical and management
activities. They are not exhaustive, but they help to achieve the outcomes in each Category.
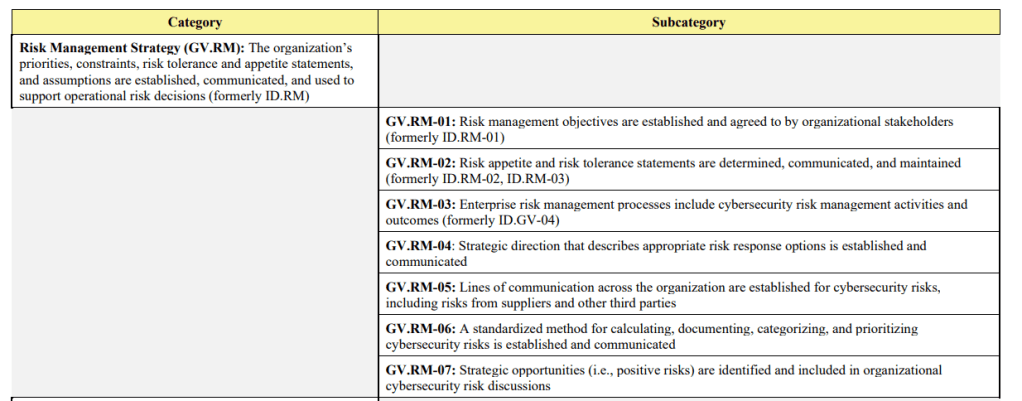
Let’s take govern for example,

Within Risk Management Strategy there are sub-categories
Implementation Examples and Informative References
Informative references
- Are standards, guidelines, regulations to help organization on how to achieve the Functions, Categories, and Subcategories (SP 800-53)
Implementation Examples
- Provides examples on how to achieve the outcomes of the subcategories
How to use the Framework
- Framework could be used based on organization risk appetite and risk expectation
- Organizations may choose to handle risk in different ways — including mitigating, transferring, avoiding, or accepting the risks depending on the potential risks.
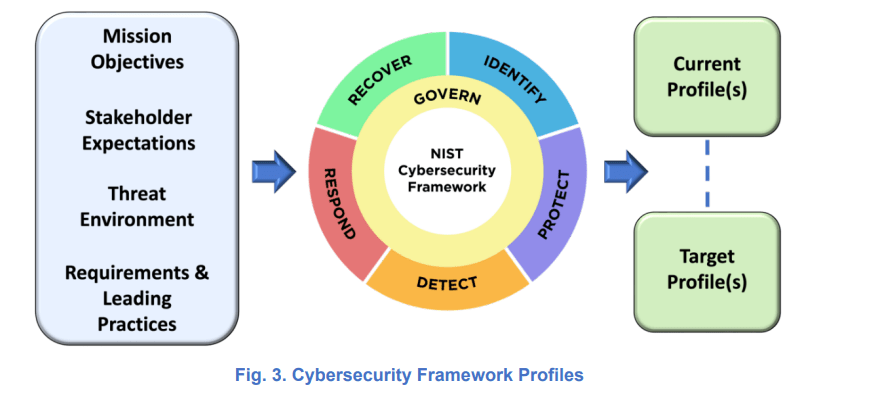
Risk Management Process
NIST2 recommends understanding the current state (Current profile) and move to Target state (Based on Mission, Expectation, Threat (Target profile)).
A Community Profile is a Target Profile created to address shared interests and goals among a group of organizations (Example Manufacturing profile).
NIST2 has provided steps on how to move from the current to target profile

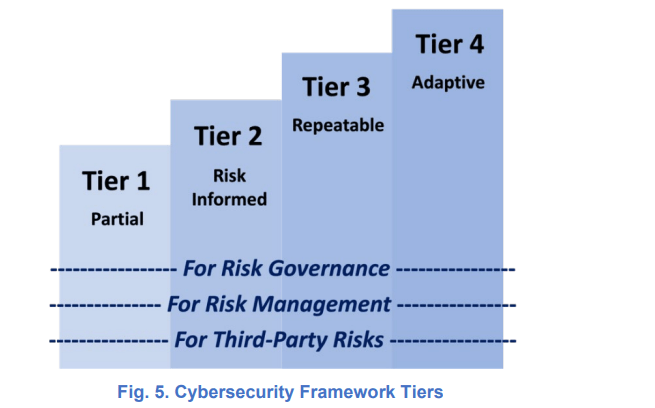
Categorizing Framework outcome using Tiers
It is important to formulate tiers based on the outcomes. Depending on the organization structure and objectives , organization can determine the tier level and also formulate roadmap to move from one tier to another tier level
Improving communication with External and Internal Stakeholders using the Framework
- Internal Stakeholders
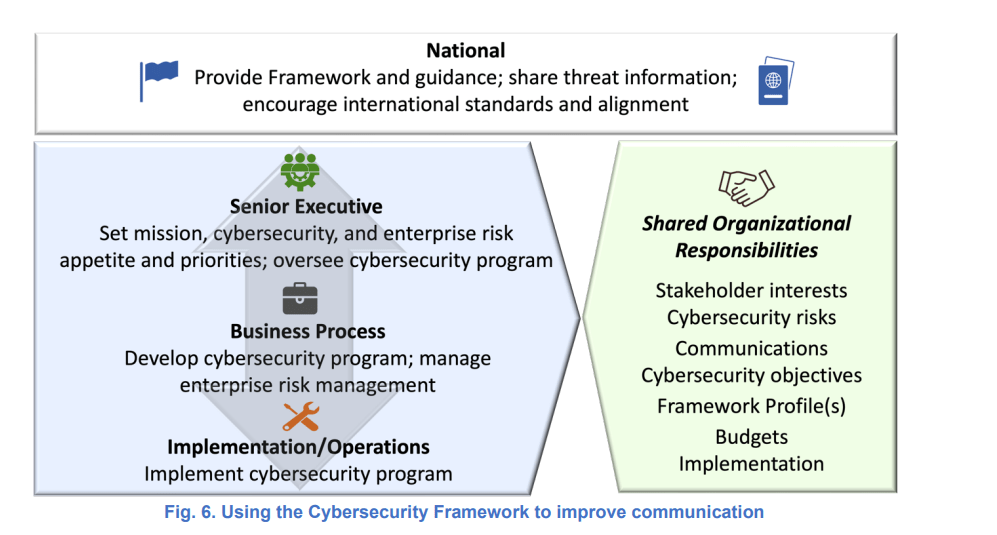
- External Stakeholders
- Providing expectation (Target profile) to their service
- Reporting to the Regulators
- Understanding priorities for the sector
- Fulfilling stakeholder expectations
- Providing cybersecurity risk reports to future customer
- Define share responsibility with the cloud service providers
Managing cybersecurity risk with the supply chain
- SCRM (Supply Chain Risk Management) is critical for organizations. Cybersecurity SCRM (C-SCRM) is a systematic process for managing exposure to cybersecurity risk throughout supply chains and developing appropriate response strategies, policies, processes, and procedures. SP 800-161r1
- Secure Software development overlaps with the SCRM SP 800-218
Integrate cybersecurity risk Management with other risk management domain with Framework

Integrate cybersecurity risk Management with other Enterprise risk management with Framework (NSIT IR 8286)
Five important step for organization to continuously improve cybersecurity posture
- Ensuring that assets that are important to the enterprise are considered when defining the Framework use case (step 1)
- Including ERM-related input (e.g., enterprise risk categories, priorities, integrated risk registers) when gathering information needed to prepare the Profiles (step 2)
- Considering tangible and assessable representation of risks (risk scenarios) from throughout the enterprise when evaluating the risk implications of the current state and defining the desired state that will address important risks (step 3)
- Ensuring that expectations from those in ERM roles (e.g., enterprise risk steering committee, senior executives, and officers) are included in the analysis and prioritization to create an action plan (step 4)
- Communicating results from action plan implementation (step 5) to those in ERM roles to help monitor cybersecurity risk strategy results, adjust that strategy to pursue opportunities, and reduce exposure throughout the enterprise.
The action plan should include metrics, such as key performance indicators (KPIs) and key risk indicators (KRIs) that help monitor, evaluate, and adjust the enterprise risk strategy. Reviews of those results, expressed in terms of business and enterprise objectives, help to maintain and adjust organizational strategy.
Summary of changes from Version 1.1 to Draft
- Recognize broad use of the Framework
- Relating CSF to other Frameworks and resources
- Increased guidance on CSF implementation
- Emphasize cybersecurity Governance
- Emphasize cybersecurity supply chain risk management
- Clarify understanding of cybersecurity measurement and assessment





Leave a comment